Describe Staretgies Sharks Use to Osmoregulate
Osmoconforming fish such as sharks maintain an internal osmolarity equal to or even higher than that of the surrounding water. The osmotic stress activates genes in certain bacteria that lead to the synthesis of osmoprotectant molecules.

Relative Importance Indicated By The Width Of Arrows Of Ecological Download Scientific Diagram
Osmoregulation Strategies of Different Organisms.
. Many teleost fishes have a large gas-filled bladder often called a swim bladder in their body cavity which eliminates the weight of the fish in water. A shark has a total ionic concentration of around 1007 mgsl. Viviparous sharks give birth to small litters typically 2-20 depending on.
However they must still maintain concentrations of specific solutes that differ from those in the external water. This simple strategy is also used by the ancient Coelcanth Latimera chalumnae. Fish are osmoregulators but must use different mechanisms to survive in a freshwater or b saltwater environments.
They loan money at very high. The shark pups will hatch inside of the womb and live off an placenta until they are ready to be born. Loan sharks are people not fish.
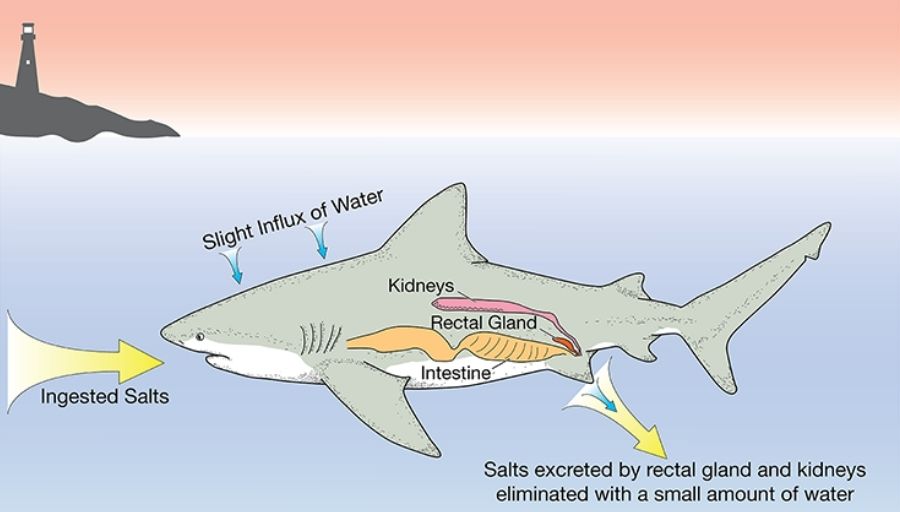
Urea damages living tissues so to cope with this problem some fish retain trimethylamine oxide. Sharks do have to deal with a slight influx of salt which is excreted by a rectal gland. How they avoid poisoning themselves with the urea is a more complicated question that is beyond the scope of this introduction but the trimethylamine oxide is an important factor.
When they are in marine environments they osmoregulate like other sharks using urea TMAO and efficient kidneys to keep an isotonic relationship with the external environment. Any changes in OPe result in changes in OPi. Osmoregulation is a process that regulates the osmotic pressure of fluids and electrolytic balance in organisms.
In most organisms the kidney regulates internal salt levels. Besides the brain osmoregulators are also. 1 Salt-in strategy in which they accumulate KCl or other salts in the cytoplasm.
Start studying AP Bio Osmoregulation and Excretion. The word shark can be used to describe someone who is tricky and uses other people. Marine sharks and most other cartilaginous fishes chondrichthyans use a different osmoregulatory strategy Like bony fishes salts diffuse into the body from seawater and these salts are removed by the kidneys a special organ called the rectal gland or in feces.
Osmoregulation is the process of maintenance of salt and water balance osmotic balance across membranes within the bodys fluids which are composed of water plus electrolytes and non-electrolytes. TMAO stabilizes proteins in the presence of high urea levels preventing the disruption of peptide bonds that would occur in other animals exposed to similar levels of urea. An electrolyte is a solute that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water.
Describe the parts of a gill. Bacteria - When osmolarity increases around bacteria they may use transport mechanisms to absorb electrolytes or small organic molecules. Urea is relatively easy to produce most organisms already make it in some form they just excrete it and.
There is always a difference between the salinity of a fishs environment and the inside of its body whether the fish. Because of this sharks are considered osmoconformers the opposite of osmoregulators. That is they actively regulate their internal salinity to match the salinity of their outside environment.
In animals this process is brought about by osmoreceptors which can detect changes in osmotic pressure. Discuss the function of the gill rakers. They retain urea in their blood in relatively higher concentration.
Organisms have two strategies to deal with salt. Osmoregulation in teleost fishes whether they live in freshwater or sea its physiological activity is very closely related to their survival yet in-spite of the importance of osmoregulation surprisingly little is known about how fish deals with physiological problems inherent in living in hypo-osmotic and hyperosmotic environments. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Describe the strategies that sharks use to osmoregulate-sharks retain urea and some salt in their blood -internal environment is hypertonic to sea water-tend to gain water so they have dilute urine. One of the ions that sharks use is urea. An example of this is the term loan shark.
Fish are osmoregulators but must use different mechanisms to survive in a freshwater or b saltwater environments. Thus they do not typically lose water. Neutrally buoyant fishes can hover in the water and swim with much less energy.
A fish is after all a collection of fluids floating in a fluid environment with only a thin skin to separate the two. A non-electrolyte in contrast does not dissociate into ions. Fish are either osmoconformers or osmoregulators.
Sharks are osmoconformers. Some marine fish like sharks have adopted a different efficient mechanism to conserve water ie osmoregulation. 2 Organic-osmolyte in strategy in which they can accumulate an.
Swim bladders of fish at depth help maintain buoyancy by regulating gas levels. For marine invertebrates this presents no problem of the open sea is a stable environment. This is usual for marine organisms.
Sharks are cartilaginous fish with a rectal gland to secrete salt and assist in osmoregulation. Sharks are cartilaginous fish with a rectal gland to secrete salt and assist in osmoregulation. These animals that secrete urea are called ureotelic animals.
The rectal gland receives hormonal inputs mainly from. Humans and most other warm-blooded organisms have osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus. Modification of work by Duane Raver NOAA.
Sharks born through viviparity will have an umbilical cord located between the pectoral fins that delivers them nutrients and oxygen from the mothers bloodstream. Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining an internal balance of salt and water in a fishs body. This means that the number of solutes inside is equal to the water around the shark.
Since their internal osmotic pressure OPi is equal to the external osmotic pressure OPe there is no need for these animals to osmoregulate and not surprisingly the majority of them lack any means doing so. Sharks are able to achieve this isotonic state because of the high concentration of urea and trimethylamine N-oxide TMAO in them. When Bull Sharks are in freshwater they basically tone down their kidneys and remove not as much salt but more urea and TMAO.
While sharks have kidneys there is an additional organ which aids in their salt regulation the rectal gland. This provides a better solution to ureas toxicity. Sharks are cartilaginous fish with a rectal gland to secrete salt and assist in osmoregulation.
Geomagnetic Orientation In Sharks Diagram Of The Induced Electric Download Scientific Diagram

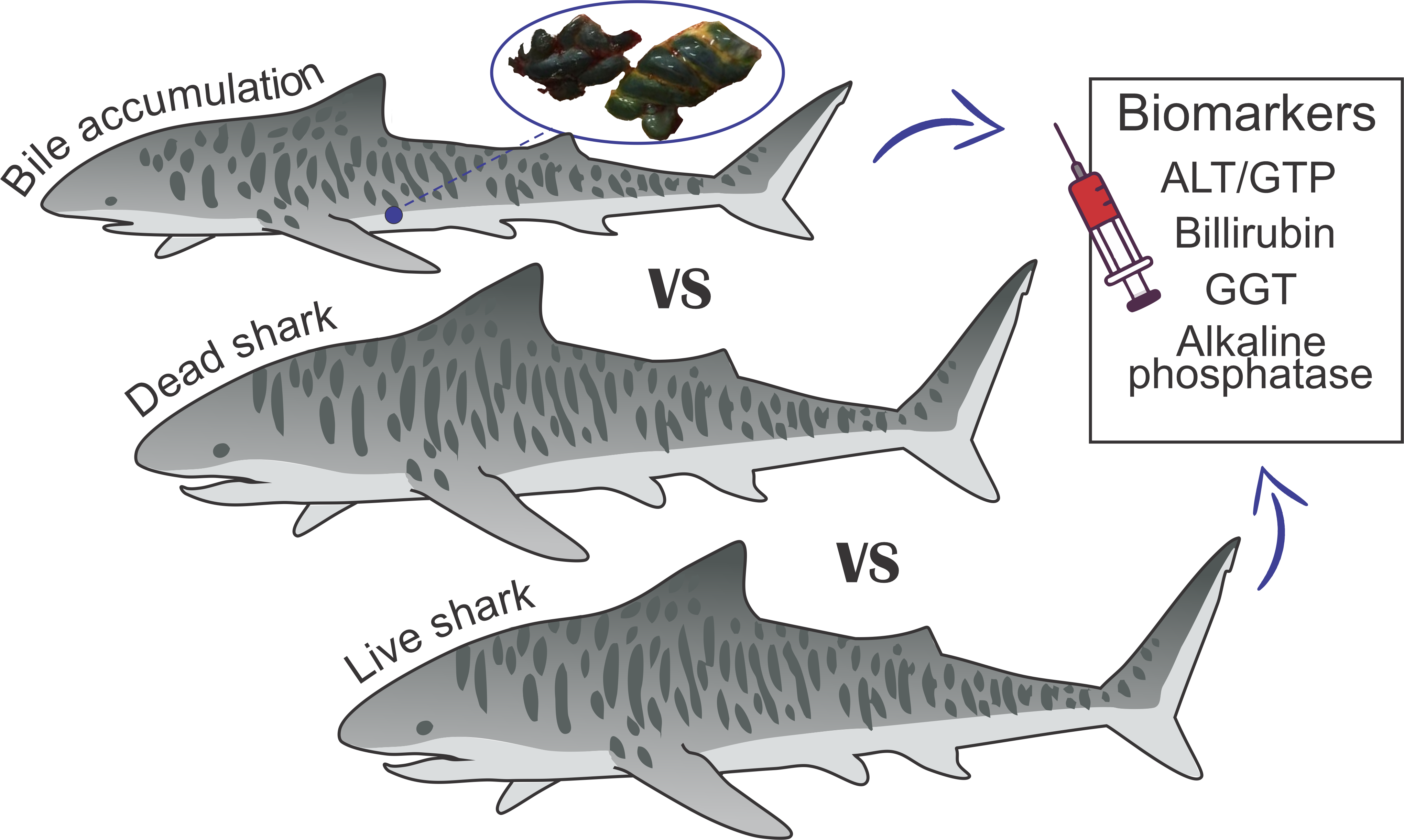
Animals Free Full Text Physiological Impairment As A Result Of Bile Accumulation In An Apex Predator The Tiger Shark Galeocerdo Cuvier Peron Amp Lesueur 1822 Html
No comments for "Describe Staretgies Sharks Use to Osmoregulate"
Post a Comment